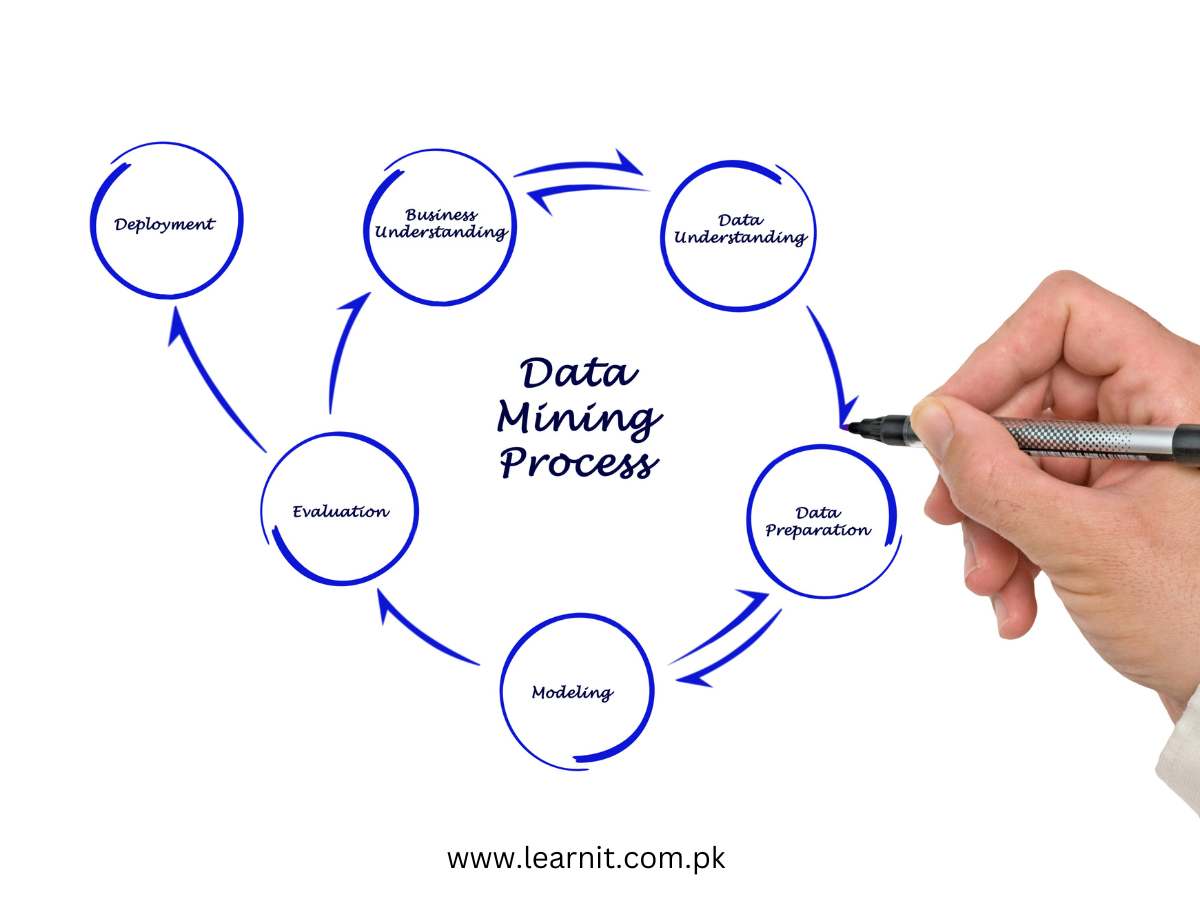
Data Sets | 30 Types of data sets in data mining

Data sets are structured collections of data points or observations that are organized and used for analysis, modeling, and research purposes. In the context of data mining, data sets serve as the foundation for discovering patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. They play a crucial role in training machine learning algorithms, testing hypotheses, and validating models. Data sets can be sourced from various domains and come in different types, each offering unique insights into specific aspects of the real world. In this article, we will explore the concept of data sets in data mining, examining the various types of data sets and providing real-life examples to illustrate their applications across diverse industries and research fields.
Cross-Sectional Data Set:
- Introduction: Cross-sectional data sets capture information from different individuals, entities, or objects at a single point in time.
- Real-life Example: A market research company conducts a survey on customer satisfaction for various mobile phone brands, collecting data from different customers at a specific moment.

Time Series Data Set:
- Introduction: Time series data sets record data points over successive time intervals, allowing analysis of trends and patterns over time.
- Real-life Example: Meteorological agencies use time series data sets to track weather conditions daily, enabling climate analysis and weather predictions.
Longitudinal Data Set:
- Introduction: Longitudinal data sets track the same individuals, entities, or objects over an extended period, enabling the study of changes and trends over time.
- Real-life Example: A medical research study follows a group of patients over several years to analyze the progression of a chronic disease and the effectiveness of treatments.
Transactional Data Set:
- Introduction: Transactional data sets record individual transactions or events, often used for market basket analysis and association rule mining.
- Real-life Example: Retailers collect transactional data sets from point-of-sale systems, allowing them to analyze customer buying patterns and optimize product placements.
Text Data Set:
- Introduction: Text data sets consist of unstructured text data, such as customer reviews, social media posts, or articles.
- Real-life Example: Social media platforms use text data sets to analyze user sentiments towards products, brands, or events, helping businesses understand public opinions.
Image Data Set:
- Introduction: Image data sets contain collections of images used for image recognition and computer vision tasks.
- Real-life Example: Autonomous vehicles use image data sets to recognize traffic signs, pedestrians, and obstacles on the road, enabling safe navigation.
Audio Data Set:
- Introduction: Audio data sets contain sound recordings and are used for speech recognition and audio processing tasks.
- Real-life Example: Virtual assistants like Siri and Google Assistant use audio data sets to understand and respond to voice commands from users.
Spatial Data Set:
- Introduction: Spatial data sets include geographic information, such as coordinates and addresses.
- Real-life Example: Urban planners use spatial data sets to analyze city infrastructure and plan efficient transportation networks.
Relational Data Set:
- Introduction: Relational data sets store data in tables with relationships between entities.
- Real-life Example: Customer relationship management (CRM) systems use relational data sets to manage customer data and track interactions.
Social Network Data Set:
- Introduction: Social network data sets represent relationships and connections between individuals or entities.
- Real-life Example: Social media platforms use social network data sets to recommend connections and identify influential users.
Sensor Data Set:
- Introduction: Sensor data sets capture data from various sensors, such as temperature, pressure, or motion sensors.
- Real-life Example: Internet of Things (IoT) devices use sensor data sets to monitor environmental conditions and control home automation systems.
Genomic Data Set:
- Introduction: Genomic data sets contain genetic information, used for genomic analysis and personalized medicine.
- Real-life Example: Genomic data sets are used in medical research to study the genetic basis of diseases and develop targeted therapies.
Financial Data Set:
- Introduction: Financial data sets include data related to financial transactions, stock prices, and economic indicators.
- Real-life Example: Financial analysts use financial data sets to analyze market trends, predict stock prices, and assess economic performance.
Healthcare Data Set:
- Introduction: Healthcare data sets contain patient records, medical images, and health-related information.
- Real-life Example: Hospitals use healthcare data sets for patient diagnosis, treatment planning, and medical research.
Marketing Data Set:
- Introduction: Marketing data sets include customer demographics, behavior, and response to marketing campaigns.
- Real-life Example: E-commerce companies use marketing data sets to target specific customer segments with personalized promotions and recommendations.
Environmental Data Set:
- Introduction: Environmental data sets capture data related to environmental factors, such as pollution levels and weather conditions.
- Real-life Example: Environmental agencies use environmental data sets to monitor air and water quality, track deforestation, and study climate change.
Geospatial Data Set:
- Introduction: Geospatial data sets include geographic information with spatial coordinates.
- Real-life Example: Mapping applications use geospatial data sets to provide directions, locate points of interest, and plan routes.
Survey Data Set:
- Introduction: Survey data sets collect data through questionnaires and interviews.
- Real-life Example: Political pollsters use survey data sets to gauge public opinion and predict election outcomes.
Web Usage Data Set:
- Introduction: Web usage data sets track user interactions on websites, such as clicks and page views.
- Real-life Example: Online retailers use web usage data sets to analyze user behavior, optimize website design, and improve user experience.
Historical Data Set:
- Introduction: Historical data sets contain past records and events.
- Real-life Example: Historians use historical data sets to study past civilizations, events, and societal trends.
Biological Data Set:
- Introduction: Biological data sets contain biological information, such as DNA sequences and protein structures.
- Real-life Example: Biologists use biological data sets to study genetic mutations, protein interactions, and evolutionary relationships.
Education Data Set:
- Introduction: Education data sets include student performance, enrollment, and demographic information.
- Real-life Example: Educational institutions use education data sets to assess student progress, identify learning gaps, and plan curriculum improvements.
Crime Data Set:
- Introduction: Crime data sets contain information on criminal activities, arrests, and incidents.
- Real-life Example: Law enforcement agencies use crime data sets to identify crime hotspots, allocate resources, and develop crime prevention strategies.
Internet Search Data Set:
- Introduction: Internet search data sets capture user search queries and behavior.
- Real-life Example: Search engines use internet search data sets to improve search results and provide relevant advertisements.
Health Records Data Set:
- Introduction: Health records data sets contain patient medical history and treatment information.
- Real-life Example: Medical researchers use health records data sets to study disease patterns, treatment outcomes, and patient demographics.
Economic Data Set:
- Introduction: Economic data sets include data on economic indicators, such as GDP, inflation, and unemployment rates.
- Real-life Example: Economists use economic data sets to analyze economic trends, forecast economic growth, and develop monetary policies.
Log Data Set:
- Introduction: Log data sets capture records of events, activities, or system processes.
- Real-life Example: IT administrators use log data sets to monitor system performance, detect anomalies, and troubleshoot issues.
Product Reviews Data Set:
- Introduction: Product reviews data sets contain customer feedback and opinions on products or services.
- Real-life Example: Product manufacturers use product reviews data sets to gain insights into customer satisfaction and identify areas for product improvement.
Inventory Data Set:
- Introduction: Inventory data sets include information on stock levels, sales, and replenishment.
- Real-life Example: Retailers use inventory data sets to optimize stock management, prevent stockouts, and reduce carrying costs.
Web Scraping Data Set:
- Introduction: Web scraping data sets are obtained by extracting data from websites.
- Real-life Example: Data scientists use web scraping data sets to gather information for research, analysis, and market intelligence.
These 30 types of data sets serve as valuable resources for data mining endeavors, illuminating the path towards discovering patterns, trends, and relationships that empower decision-making, drive innovation, and propel progress across a myriad of industries and research domains. As data-driven approaches continue to shape our world, the significance of these data sets in unlocking the potential of data mining cannot be overstated.